Table of Contents
Windows plays a vital role in optical systems in reducing reflection, maximizing transmission, and protecting electronic sensors and optical systems from any environmental factor. When the conditions are harsh, considering a robust material is essential. That is why we will look at a very robust sapphire window.

Why a sapphire window?
Sapphire (Al203) is a durable crystal material that comes second after diamonds when comparing their natural substrate ratings. Sapphires have 9 Mohs hardness making them one of the most rigid materials. Windows or optical components outperform silica and quartz in terms of comparison range.
So, why select Sapphire Optical Window?
Properties of sapphire window
Before we look at Windows properties, let’s see why sapphire. Various features of sapphires make them best for windows. It includes;
- It’s excess surface hardness and structure integrity
- Unique resistance to scratching and abrasion
- Has high mechanical strength
- Chemically unreactive and resistant to all chemicals except hot caustics
- Has high thermal conductivity
- Offers wide optical transmission from UV to mid-IR
Let’s now look at sapphire window properties
Optical windows are used to protect the components within the instrument laser or optical assembly. They are expected to withstand harsh conditions and offer high-performance levels and reliability in some instances. For this to happen, there are various properties linked to it.
- When exposed to UV light, sapphire optical windows do not darken and lose their brilliance.
- Sapphire optical windows can withstand high temperatures if compared to other optical windows.
- It has excellent thermal conductivity and high thermal stability, making it perfect for high-power applications.
- It provides wider band transmission from UV to Mid-IR
- Also, they are resistant and stable to any strong acid attack because of sapphire’s dielectric constant
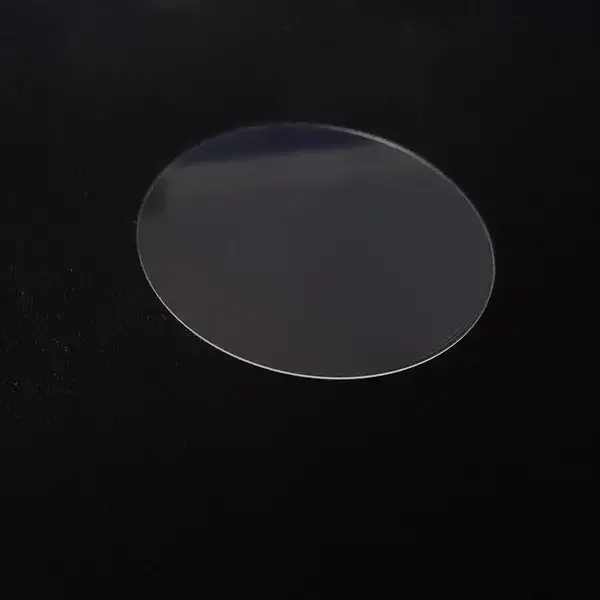
Sapphire Window Fabrication
Various sapphire growth methods are used with different specifications like size, inclusions, and thickness.
Crystal Orientation of sapphire windows
The characteristics of sapphire optical windows are determined by crystal orientation. Selecting your crystal orientation depends on various factors like thermal expansion, birefringence, and any other crystal orientation depending on physical properties.
For instance, C-plane is considered the typical sapphire optical windows material. C-plane sapphire is somehow birefringent and at times specialized as zero degrees in a window. Most optical windows need low birefringence, thus making the c-plane the ideal material.
However, if there is no specified material, Random is the default choice for optical windows. At this stage, windows get fabricated without any crystalline orientation concern known as a random cut. This is approximately 60 degrees to the optic axis, and it’s the softest saw direction.
Sapphire window polishing
Because of sapphires’ high mechanical strength and hardness, sapphire window polishing is a little difficult and slow. Developing a production process for optical windows with low scatter surface finish, optical flatness, and surface damage, it can be challenging.
Sapphire window coating
Sapphire optical windows coating uses range from defense and aerospace to medical devices and sensors and instrumental. As seen at the sapphire features above, sapphire windows have to demonstrate superior performance and work under harsh conditions. That means the coating used has to withstand all extreme operating operations. The coating design needs to be multispectral, thus taking advantage of sapphire’s wide-wavelength transmission property.
Applications of a sapphire window
All the properties listed above make sapphire optical windows suitable for chemical, extreme mechanical and, optimal applications. Besides, it can be metalized to create sealed optics ideal for vacuum and harsh applications.
Because of its high strength, scratch resistance, purity, temperature resistance, and good transmission bandwidths, synthetic sapphire is the best material for laser, medical, industrial, and defense applications.
So, what is a sapphire optical window used for?
A sapphire window is ideal for various industrial applications. This is due to their structural integrity to endure extreme temperature and pressure environments. Due to its capability of remaining chemically inert, sapphire optical windows have been used in various applications. Some of its common uses include;
- submarine glass
- barcode readers
- military-grade lasers
- aerospace windows
- endoscopic instruments
- furnace viewports
- drilling vision systems
- gunsights
- microscope lenses and slides
Recently, sapphire has been a common material used wisely in fragile applications like camera lenses, cell phones, and other consumer technology areas. Looking at its production cost, the production costs will lower as the new manufacturing processes and more sapphire optical windows will help decrease the production cost. This means the sapphire window will be less expensive and, therefore, more available.
As the production costs are lower, this technology will first be tested on microscopes, cell phones, computers, and camera lenses. Also, other technologies are expected to come out, thus replacing silica-based glass.
What makes the sapphire window a high performer?
Sapphire Optical Window is a top performer because of its ability and versatility to withstand extreme conditions in any industry.
The sapphire optical window is a high performer because of its ability to withstand abrasive applications but provide optical clarity in all its applications.
Sapphire crystals are lab-created, thus allowing the analytical components to shape in their form as required for individual applications before polishing and grinding the final product. The lab-grown sapphire method is robust like raw sapphire, which reduces supply parts costs.
Another thing is sapphire is wear-resistant and, therefore, long-lasting enough before the need for replacement. Thus consumers will cut costs by minimizing replacements and repair downtime.
Also, a sapphire optical window doesn’t warp or bend when exposed to extreme heat and cold and high pressure. This makes them suitable for various applications, from molten metal containment to cryogenics and submarine equipment.
When exposed to abrasives such as small particulates of sand and many caustic chemicals, a sapphire window may start to wear to preserve the glass’s clarity.
The key feature of a sapphire window
Grades of quality
A custom sapphire window is graded on a scale of 1 to 6 to define various optical and physical properties. Grade 1 is the purest form free from microbubbles, insertions, block boundaries, and scattering. It’s also referred to as optical quality windows. These are the ideal selections for optical applications. However, sapphire optical window light scatter doesn’t matter in mechanical applications.
Optical window properties
Sapphires are robust enough to withstand weather conditions when formed into a window. Especially when providing clear optical viewpoint in various industrial applications. Higher-grade quality windows are purer and offer better precise optical applications.
Conversely, lower grades are strong but can show impurity signs. Lower-grade windows are suitable for mechanical applications where optical viewing isn’t necessary. But for sapphire windows, the glasses, microscopes, observation barriers, and windshield are essential.
Surface flatness of windows
A glass surface flatness is for performance in optical applications. We can define surface flatness as how the surface conforms to the expected shape. So, flatness can help grade how the window contours to a specific shape of the final product. Flatness is measured using a short-wavelength surface for high precision.
0