The basic structure of the capacitive touch screen is: The substrate is single-layer plexiglass, and A layer of transparent conductive film is uniformly forged on the inner and outer surfaces of the plexiglass. A long and narrow electrode is tapered on the four corners of the transparent conductive film on the outer surface.
Its working principle is: When the finger touches the capacitive touch screen, connect this time, the finger and the working surface of the touch screen form a coupling capacitor, This is equivalent to a conductor Because there are high-frequency signals on the working surface. When the finger is touched, a small current is drawn at the touchpoint. This small current flows from the electrodes on the four corners of the touch screen. The current flowing through the four electrodes is proportional to the straight line distance from the finger to the four corners, The controller calculates the ratio of the four currents, Then the coordinate value of the contact point can be obtained.
The capacitive touch screen can be simply seen as a screen composed of four layers of composite screens. The outermost layer is a protective glass layer. Next is the conductive layer, and The third layer is the non-conductive glass screen. The fourth innermost layer is also conductive. The innermost conductive layer is the shielding layer. Play the role of shielding internal electrical signals, The conductive layer in the middle is the key part of the entire touch screen. There are direct leads on the four corners or four sides. Which are responsible for detecting the position of the touchpoint.
The uppermost covering layer is tempered glass or polyethylene terephthalate (PET). The advantage of PET is that the touch screen can be made thinner, On the other hand, it is cheaper than the existing plastic and glass materials. The insulating layer is glass (0.4-1mm), organic film (10-100um), adhesive, and the air layer. The most important layer is the indium tin oxide (ITO) layer. The typical thickness of ITO is 50-100nm, Its sheet resistance is in the range of about 100 to 300 ohms.
The process and three-dimensional structure of ITO have a great influence on capacitive touch screens. It is directly related to the two important capacitance parameters of the touch screen: inductive capacitance (finger and upper ITO) and parasitic capacitance (between the upper and lower ITO, and between the lower ITO and the display screen).
The structure of the capacitive touch screen is mainly to plate a transparent film body layer on the glass screen. Add a piece of protective glass to the conductor layer. The double glass design can completely protect the conductor layer and the sensor, and at the same time, the light transmittance is higher. It can also better support multi-touch.
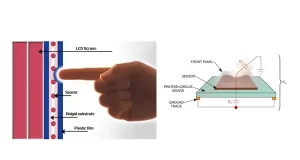
The capacitive touch screen is plated with long and narrow electrodes on all four sides of the touch screen. A low-voltage AC electric field is formed in the conductive body. When touching the screen. Due to the electric field of the human body, the Shape between the finger and conductor layer is a capacitive touch screen.
In a coupling capacitor, The current from the four electrodes will flow to the contacts. The current strength is inversely proportional to the distance between the finger and the electrode. The controller located behind the touch screen will calculate the ratio and strength of the current. Accurately calculate the location of the touchpoint.
The double glass of the capacitive touch screen can not only protect the conductor and the sensor. More effectively prevent external environmental factors from affecting the touch screen, Even if the screen is dirty, dusty, or oily. The capacitive touch screen can also still accurately calculate the touch position. Since the capacitance varies with the contact area and the dielectric of the medium, its stability is poor, Often a drift phenomenon occurs.
0











